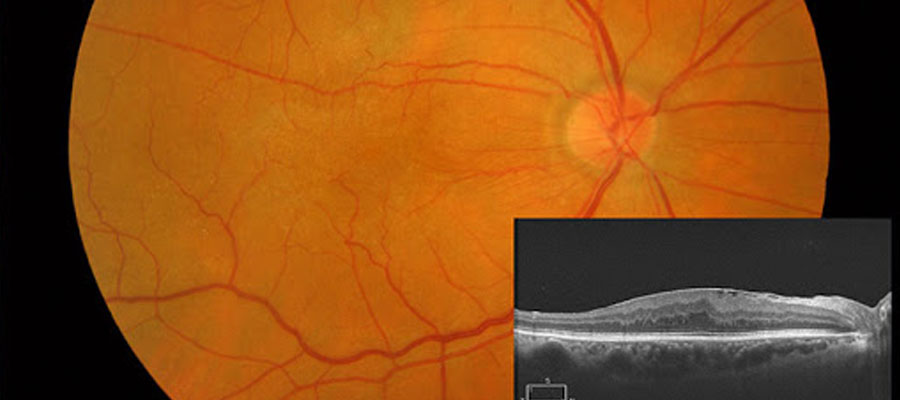
What is the epiretinal membrane?
 Epiretinal Membrane; The Macula is the name of the place in the center of the retina, which is the nerve layer of our eye, it is also called the yellow spot. For a clear vision to be formed, the macula must be in its natural shape.
Epiretinal Membrane; The Macula is the name of the place in the center of the retina, which is the nerve layer of our eye, it is also called the yellow spot. For a clear vision to be formed, the macula must be in its natural shape.
The thin membranous tissue formed on the macula is called the epiretinal membrane. This membrane wrinkles over time and distorts the shape of the macula. This causes complaints such as distorted and blurred vision. Although it is usually in one eye, it can be detected in both eyes at a rate of 10-20%.
In whom and why does the epiretinal membrane occur?
The epiretinal membrane often develops due to changes in the normal aging process in the eye. In fact, in healthy individuals, there is a 2% risk of development over the age of 50, and 20% over the age of 70.
However, it is usually not noticed because it does not cause a complaint and is often detected during routine eye examination.
Apart from age-related changes, it can develop after diabetes, uveitis (eye inflammation), trauma, retinal vascular occlusions and retinal tears and detachments.
What symptoms occur in the epiretinal membrane?
 The epiretinal membrane causes no complaints in the early stages and is usually detected during routine eye examination. The disease progresses very slowly and the appearance of visual complaints can sometimes take years.
The epiretinal membrane causes no complaints in the early stages and is usually detected during routine eye examination. The disease progresses very slowly and the appearance of visual complaints can sometimes take years.
It can cause complaints such as blurred vision, curved and wavy vision, seeing the dimensions of objects different (larger or smaller) than they are. As the disease progresses, the level of vision decreases.
One of the reasons for the late appearance of the complaints is that the healthy eye balances the vision since the disease affects only one eye.
How is the diagnosis of epiretinal membrane made?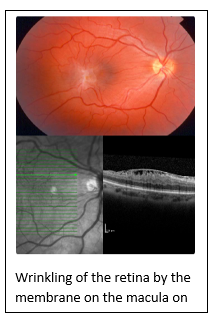
After the routine eye examination, the pupils are dilated with drops and the back of the eye (macula) is examined with special lenses.
If an epiretinal membrane is suspected, your doctor may perform an optical coherence tomography (OCT-eye tomography) examination.
By means of this examination, the size of the epiretinal membrane, the vitality of the visual cells can be interpreted and an idea about the recovery process can be obtained after the treatment.
OCT examination is also used in surgical planning.
What is the treatment of epiretinal membrane?
Since the epiretinal membrane does not cause any complaints or damage in the early stages, it is followed only by OCT film and visual examination.
Sometimes it takes years before treatment is needed. When the membrane wrinkles over time and begins to affect the visual cells, the need for treatment arises. The only treatment for epiretinal membrane is vitrectomy surgery.
In this surgery, the eye gel is cleaned by entering the eye with very small surgical instruments and the membrane causing the disease is peeled off. Surgical success rates are quite high, and the increase in vision will occur within weeks and months. Very rarely, the membrane may recur, and in this case, the patient can be operated again.
The risk in epiretinal membrane surgery is as low as 1%.