What is cataract? In whom does cataract occur? And what are the causes?
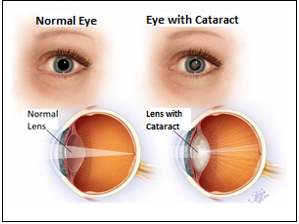 Cataract treatment is a disease of the eye lens (lens), which is located just behind the pupil and allows the image to be focused on the eye.
Cataract treatment is a disease of the eye lens (lens), which is located just behind the pupil and allows the image to be focused on the eye.
The lens of the eye is a transparent structure made up of proteins. As age progresses, the structure of these proteins changes and they lose their transparency. As a result, light reaches the back of the eye more difficult.
The loss of transparency and clouding of the lens is called cataract. Although cataract is usually seen in advanced ages, it can also be seen in young and middle ages and sometimes it can be congenital.
The most common cause of cataract is the change in the structure of the eye lens with advancing age. Moreover, some metabolic diseases such as diabetes can occur with long-term use of certain drugs, and after trauma.
What are the symptoms of cataract and what complaints does it cause?
 The lens whose transparency deteriorates becomes opaque, discolored and sometimes frosted glass. Cataract can progress for many years without any complaints.
The lens whose transparency deteriorates becomes opaque, discolored and sometimes frosted glass. Cataract can progress for many years without any complaints.
But when it progresses to a certain level, complaints begin to appear. The most common symptom is blurred vision.
However, it may cause complaints such as glare, dull vision of objects, and forked vision in bright or sunny weather.
Since the refraction of the lens also changes, there can be a rapid change in the number of glasses. Sometimes patients say they no longer need glasses for near reading. However, this is a temporary situation and after a while, patients also see blurred vision for near objects.
If the cataract is not treated and waited for too long, the lens becomes completely dull and can cause serious vision loss.
How is cataract treated? Can cataract development be prevented?
There is no treatment to prevent or stop the development of cataracts. However, limiting smoking, reducing exposure to ultraviolet rays, regular check-ups of patients using certain drugs, and regulating medications when necessary may slow down the development of cataracts.
The only treatment method for cataract is surgery. There is no treatment other than surgery. Here, the method is to remove the patient’s opaque lens and replace it with an artificial transparent lens. There are also several surgical methods.
One of them is PECCE (planned extracapsular cataract extraction), which is an old technique, and is also known as suture surgery among the people, and the other is phacoemulsification, which is also known as laser surgery, in other words PHACO surgery. Additionally, laser cataract surgery, which has become popular in recent years, is also performed.
When should the surgery be done? Is it necessary to wait for the cataract to harden?
When determining the appropriate time for cataract surgery, the social needs of the patient should be taken into account, which may differ from person to person. If the cataract has deteriorated enough to affect the patient’s vision and daily life, it is time for surgery.
After that, there is no point or benefit in delaying the surgery anymore. In phaco surgery performed in the early period, both the operation and the recovery process are easier and shorter.
If cataract surgery is delayed for too long, the surgery will become more difficult, and excessive swelling of the lens will cause an increase in eye pressure and cause serious and irreversible vision loss.
If the patient has cataracts in both eyes, should both eyes be operated at the same time or should there be a waiting period between the two?
Although cataracts affect vision at different levels, it usually happens in both eyes. Even if both eyes have cataracts at the surgical level, surgery should not be performed at the same time.
The most important factor determining the time between two surgeries is the recovery status of the first surgery. Some surgeons operate on the second eye 3 days later, while others prefer to wait up to 1 month. This completely depends on the preference of the patient and the surgeon.
Which tests are done before cataract surgery? If patients have other diseases, what should be considered before surgery?
First of all, patients should be given a complete eye examination and it should be determined whether there is a disease that prevents them from undergoing surgery. For example, in cases such as uveitis, eye pressure or glaucoma, that disease should be treated first and cataract should be considered as a priority only if it prevents the treatment of that disease.
Additionally, measurement is made to determine the number of the lens to be inserted into the eye. Apart from that, we do some simple blood tests for the patients before the surgery.
hese tests are performed both to determine whether the patients have a condition that prevents surgery and to determine whether they carry certain diseases such as the jaundice virus. Because if carrier is detected, this is not an obstacle to surgery, but we need to take the necessary precautions to prevent contagion.
Patients may have some systemic diseases and these patients should continue their normal treatment. The only exception is for patients taking blood thinners. These patients may have to interrupt or change their medications, if necessary, as recommended by the physician.
Can you give information about the phaco method? What are the advantages?
Although PHACO surgery is known as laser cataract surgery among the people, it is actually the cleaning of the cataractous lens with the help of a pen-like instrument whose tip vibrates with high-frequency sound waves.
Today, it is the golden standard in cataract surgery and is the most successful method among all surgical procedures. During this procedure, the eye is anesthetized with only drops and the cataract is cleared by entering the eye through an incision of approximately 2-3 mm.
An artificial lens is then placed in the eye. Because the incision is very small, no sutures are required. The operation takes about 10 minutes, the recovery process is very fast, and the complication rate is very low.
Is it absolutely necessary to put a lens on the patient? Does the quality of this lens affect the outcome of the surgery?
Lens attachment is an integral part of phaco surgery. The aim is to replace the opacificating lens with a new transparent lens. This lens will remain in the eye for a lifetime. The lens to be attached to the eye is one of the factors that affect the result of the surgery, that is, vision.
Therefore, the lens to be attached must be of certain standards for a clear vision. Some lenses only show far, while others have features that show both near and far. Also, some lenses correct a kind of eye disorder called astigmatism
What kind of process awaits the patients after the surgery? How is the recovery process? What should discharged patients pay attention to?
Recovery process after PHACO surgery is very rapid. The patient’s eyes are kept closed for 1 night, according to the physician’s preference. Some physicians do not consider it necessary to close the eye. Although the restrictions vary according to the preference of the physician, the patient can do his daily activities 1 day after the surgery.
In the postoperative period, the patient should use antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops for one month. Apart from this, no other medication is needed.
Controls are usually done on the 1st day, 1st week and 1st month. If the patient has complaints such as severe pain in the eye, sudden clouding, swelling of the eyelid, he should consult the physician immediately.
Do patients need to wear glasses in the postoperative period? If necessary, how long after the operation are glasses given?
The lens placed in the eye during surgery is corrective lens. The number of this lens is calculated with special devices before the surgery.
If this calculation is correct and the lens that is attached to the patient’s eye is a type that only corrects distance vision, the patient does not need distance glasses. Also, some lenses correct a kind of eye disorder called astigmatism. But the patient needs to use reading glasses.
If the lens used is a type that shows both far and near, the patient does not need to wear glasses for life. Full fixation of the refraction, that is, the visual impairment, may take 3-4 weeks.
Will cataract develop again in a patient who has had cataract surgery?
Cataract surgery is a once-in-a-lifetime surgery. Cataract does not develop again. However, the lens to be inserted into the eye during surgery is placed in a membrane.
This normally transparent membrane loses its transparency over the years and can become dull and distort the vision. If this occurs, this membrane is punctured with a simple procedure in outpatient clinic conditions with the help of laser beam and the patient regains clear vision.






